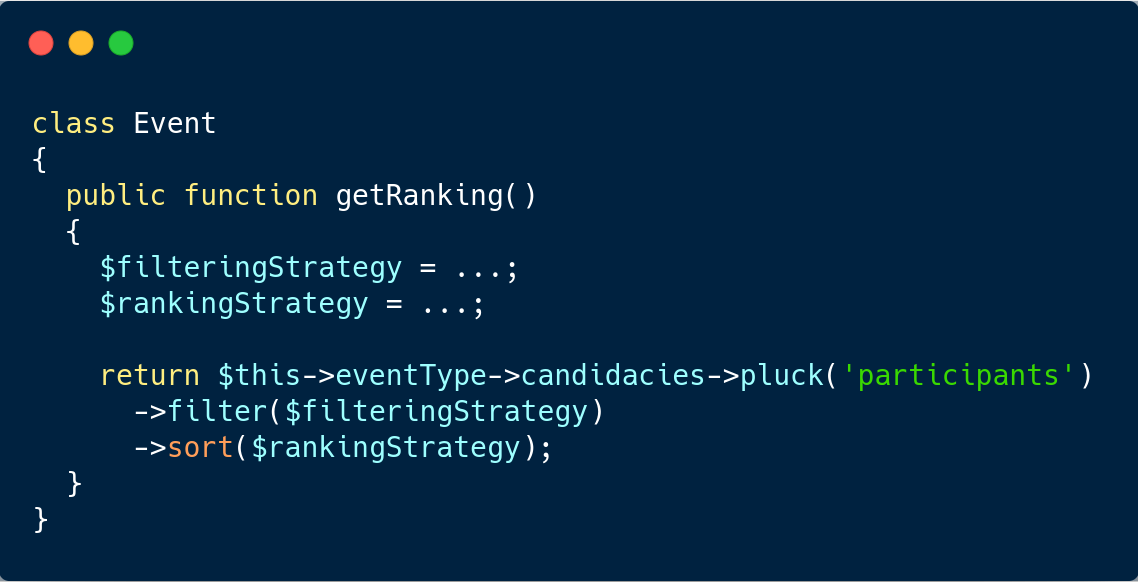
Create LazyCollection from API resource
Laravel 6 introduced the LazyCollection, a different kind of collection which exploits php generators to save memory usage. While data fetching from database is natively managed by eloquent, Web API-based data fetching is not provided. This article describes how to use a paginated api endpoint to fetch data to a LazyCollection instance.
Tags:
Laravel
api
PHP
generators

Related posts